Module: pinholeCamera
Executive Summary
This module simulates a camera pinhole model that computes landmark pixels as seen by a spacecraft. It reads the planet’s ephemeris and spacecraft state messages as inputs. It outputs a vector of landmark messages.
The module can also account for Sun’s lighting constraint by setting a mask angle.
Module Assumptions and Limitations
The module assumes a landmark is characterized by its position and surface normal (to check field of view and lighting conditions). Diffuse reflection of the light is assumed thus the reflected ray is aligned with the surface normal. Under the previous assumptions, the landmark can be thought as an infinitesimal surface element.
The pinhole camera model lacks ray-tracing capabilities. Consequently, when using a landmark distribution based on a non-convex shape, it is possible that false positives occur. This means that landmarks that are not visible can be marked as such.
Message Connection Descriptions
The following table lists all the module input and output messages. The module msg variable name is set by the user from python. The msg type contains a link to the message structure definition, while the description provides information on what this message is used for.
Msg Variable Name |
Msg Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ephemerisInMsg |
planet ephemeris input message. |
|
scStateInMsg |
vector of sc state input messages. |
|
landmarkOutMsgs |
vector of landmark messages. |
Detailed Module Description
The pinholeCamera module handles the following behavior:
Reads in the spacecraft’s state using the
scStateInMsgand planet’s ephemeris using theephemerisInMsginput messageComputes spacecraft position
r_BP_Pand orientation with respect to planet framedcm_BP. It also computes planet to Sun’s unit-vector in planet framee_SP_P.It loops through each landmark determining if it is within camera field of view and illuminated by Sun.
If the previous conditions are met, the landmark pixel is saved.
It writes a vector of
landmarkOutMsgsmessages for each landmark.
Determining Landmark Pixels
By assuming \(z\) as the focal direction, the pinhole camera model maps a 3D point to 2D image plane coordinates as:
Since the image is digital, the pixel is defined by
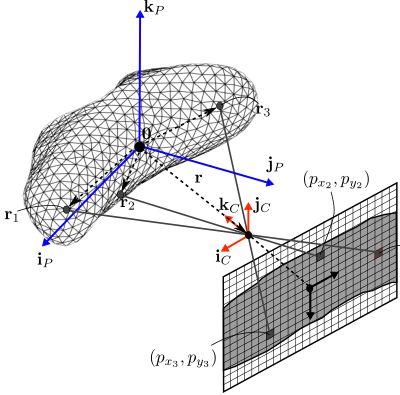
Figure 1: Diagram of pinhole camera
A landmark is marked as visible if it pass the subsequent checks. The first check is that the landmark is illuminated by the Sun, thus
where \(\mathbf{e}^{P}_{SP}\) is planet to Sun unit-vector, \(\mathbf{n}^{P}_{L}\) is the landmark normal and \(\theta_{Sun}\) Sun’s mask angle.
The following checks first filter landmarks that are behind the camera focal direction \(\mathbf{k}^{P}_{C}\). Then, it eliminates the landmarks that do not reflect light to the camera:
where \(\mathbf{k}^{P}_{C}\) is the camera focal direction and \(\mathbf{e}^{P}_{BL}\) is the unit-vector from landmark to spacecraft.
Finally, for the remaining landmarks, the ones that are not within camera field of view are also eliminated.
User Guide
To use this module, instantiate the class and provide it with camera parameters and a landmark distribution. The camera parameters comprise: horizontal number of pixel; vertical number of pixel; pixel width; focal length; direction cosine matrix of camera w.r.t. body frame; Sun’s mask angle (optional). The landmark distribution is added using the addLandmark(pos, normal) method. The module has to be subscribed to a planet ephemeris message EphemerisMsgPayload and a spacecraft state message SCStatesMsgPayload.
An instance of pinholeCamera, alongside necessary user-supplied parameters, can be created by calling:
camera = pinholeCamera.PinholeCamera()
camera.ModelTag = "camera"
camera.nxPixel = 2048 # Sets number of horizontal pixels
camera.nyPixel = 1536 # Sets number of vertical pixels
camera.wPixel = (17.3*1e-3)/2048 # Sets pixel width
camera.f = 25*1e-3 # Sets camera focal length
camera.maskSun = 0*np.pi/180 # Sets Sun's mask angle (optional)
camera.dcm_CB = [[0,0,-1],[0,1,0],[1,0,0]] # Sets dcm of camera w.r.t. spacecraft body (focal direction is [0,0,1] in camera frame)
for i in range(n_lmk):
camera.addLandmark(pos_lmk[i, 0:3], normal_lmk[i, 0:3]) # Adds a landmark
camera.ephemerisInMsg.subscribeTo(ephemConverter.ephemOutMsgs[0]) # Sets planet ephemeris message
camera.scStateInMsg.subscribeTo(scObject.scStateOutMsg) # Set spacecraft state message
scSim.AddModelToTask(simTaskName, camera)
The maskSun variable is optional and defaults to -90º. This means by default the entire surface is lighted. Set it to a positive value to consider the lighting constraint.
The processBatch(rBatch_BP_P, mrpBatch_BP, eBatch_SP_P, show_progress) method allows to execute the module detached from the SimulationBaseClass. It can be called as:
# Preallocate output pixels
pixelBatchLmk = np.zeros((n, n_lmk, 2))
# Process pinhole camera as a batch
e_SP_P = -r_PN_P / np.linalg.norm(r_PN_P, axis=1)[:, None] # Unit-vector from planet to Sun
camera.processBatch(r_BP_P, mrp_BP, e_SP_P, True) # Execute method (last argument is a bool, when True it shows progress status)
isvisibleBatchLmk = np.array(camera.isvisibleBatchLmk) # Save visibility status
pixelBatchLmk[:, :, 0] = np.array(camera.pixelBatchLmk)[:, 0:n_lmk] # Save px
pixelBatchLmk[:, :, 1] = np.array(camera.pixelBatchLmk)[:, n_lmk:2*n_lmk] # Save py
-
class PinholeCamera : public SysModel
- #include <pinholeCamera.h>
Pinhole camera class.
Public Functions
-
PinholeCamera()
Creates an instance of the PinholeCamera class with a prescribed focal direction in camera frame and -90º of Sun’s mask angle (that is, no lighting constraint).
- Returns:
void
-
~PinholeCamera()
Empty destructor method.
- Returns:
void
-
void UpdateState(uint64_t CurrentSimNanos)
Update module
- Parameters:
CurrentSimNanos –
-
void Reset(uint64_t CurrentSimNanos)
Resets the module.
-
void readInputMessages()
Read module input messages
-
void writeOutputMessages(uint64_t CurrentClock)
Write module output messages
-
void addLandmark(Eigen::Vector3d &pos, Eigen::Vector3d &normal)
Method to add landmarks
- Parameters:
pos – landmark position in planet-rotating frame
normal – landmark surface normal in planet-rotating frame
-
void processBatch(Eigen::MatrixXd rBatch_BP_P, Eigen::MatrixXd mrpBatch_BP, Eigen::MatrixXd eBatch_SP_P, bool show_progress)
Process a batch of inputs: spacecraft positions, orientation and unit-vector from planet to Sun.
- Parameters:
rBatch_BP_P – batch of spacecraft position w.r.t. planet in planet-rotating frame
mrpBatch_BP – batch of spacecraft MRPs w.r.t. planet-rotating frame
eBatch_SP_P – batch unit-vectors from planet to Sun in planet-rotating frame
show_progress – boolean variable that prints batch processing status when true
Public Members
-
double f
[m] camera focal length
-
double FOVx
[rad] horizontal field of view
-
double FOVy
[rad] vertical field of view
-
double nxPixel
[-] number of horizontal pixels
-
double nyPixel
[-] number of vertical pixels
-
double wPixel
[m] pixel width
-
Eigen::Matrix3d dcm_CB
[-] dcm from body to camera
-
Eigen::VectorXi isvisibleLmk
[-] flag telling if a landmark is visible
-
Eigen::MatrixXi pixelLmk
[-] pixels for landmarks
-
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> r_LP_P
[m] landmark positions in planet frame
-
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> nL_P
[-] landmark normals in planet frame
-
double maskSun
[-] minimum slant range for Sun lighting
-
ReadFunctor<EphemerisMsgPayload> ephemerisInMsg
planet ephemeris input message
-
ReadFunctor<SCStatesMsgPayload> scStateInMsg
spacecraft state input msg
-
SCStatesMsgPayload spacecraftState
input spacecraft state
-
EphemerisMsgPayload ephemerisPlanet
input planet ephemeris
-
std::vector<Message<LandmarkMsgPayload>*> landmarkOutMsgs
vector of landmark messages
-
std::vector<LandmarkMsgPayload> landmarkMsgBuffer
buffer of landmark output data
-
BSKLogger bskLogger
— BSK Logging
-
Eigen::MatrixXi pixelBatchLmk
[-] batch of landmark pixels
-
Eigen::MatrixXi isvisibleBatchLmk
[-] batch of landmark visibility stauts
Private Functions
-
void processInputs()
Process input messages to module variables
-
void loopLandmarks()
Loop through landmarks
-
bool checkLighting(Eigen::Vector3d nLmk)
Check lighting condition of a landmark
- Parameters:
nLmk – landmark surface normal in planet-rotating frame
-
bool checkFOV(Eigen::Vector2i pLmk, Eigen::Vector3d rLmk, Eigen::Vector3d nLmk)
Check if a landmark is within camera field of view
- Parameters:
pLmk – landmark pixel
rLmk – landmark position in planet-rotating frame
nLmk – landmark surface normal in planet-rotating frame
-
Eigen::Vector2i computePixel(Eigen::Vector3d rLmk)
Compute pixel from 3D coordinates
- Parameters:
rLmk – landmark position in planet-rotating frame
Private Members
-
int n
[-] number of landmarks
-
Eigen::Vector3d r_PN_N
[m] current planet position in inertial frame
-
Eigen::Vector3d r_BP_P
[m] current spacecraft position w.r.t. planet in planet frame
-
Eigen::Matrix3d dcm_BP
[-] current direction cosine matrix from planet to spacecraft body frame
-
Eigen::Matrix3d dcm_PN
[-] current direction cosine matrix from inertial to planet frame
-
Eigen::Vector3d e_SP_P
[-] current unit-vector pointing from planet to Sun in planet frame
-
Eigen::Vector3d eC_C
[-] focal direction unit-vector in camera frame
-
Eigen::Vector3d eC_P
[-] focal direction unit-vector in planet frame
-
PinholeCamera()