Installing On macOS¶
These instruction outline how to install Basilisk (BSK) on a clean version of macOS. The preferred method is to use Python 3. For now support is also provided to use the built-in Python 2, but Python 2 support is now a depreciated functionality.
Developer Software Tools¶
In order to run Basilisk on macOS, the following software is necessary:
Get the Apple Xcode Developer tool from the App Store
After Xcode is installed, start up the program to let it finish installing development components
Open a Terminal window to install the command line tools using:
$ xcode-select --install
Get the CMake application to be able to create the Xcode IDE file
You will need the command line version of
cmakeas well. To see if you have it already installed, typewhich cmakeinto the terminal and you should an output like/usr/local/bin/cmake. If you get no response, then you need to installcmake. Here are two options:The CMake.app contains instruction on how to install the command line version inside the Tools menu.
As an alternate approach, you can also install using homebrew as described below
(Optional) Get the SourceTree application to be able to pull and manage a copy of Basilisk
(Optional) Get the PyCharm application to be able to edit python source files
Choosing Python 3 (preferred) or Python 2 (depreciated) setups¶
Basilisk is able to create both Python 3.7 or Python 2.7 code. All the unit test and tutorial scenario files are written such that they work in both generations of Python. The Python 3 version is the preferred installation method. Python 2 remains supported, but should be treated as depreciated.
To install Python 3 on macOS there are two common options:
Download the installer package from python.org
Install python 3 through the HomeBrew package management system. The site has the command line to install homebrew from a terminal window.
Install HomeBrew Support Packages¶
Install HomeBrew using a Terminal window and pasting the install script from the HomeBrew web site.
Note
This must be done within a
bashterminal window. The type of terminal emulation is shown on the top of the terminal window. If you are running another terminal type, typebashto engage the Bash terminal environment. This is just required to install HomeBrew. Once it is installed, you can run all other commands from any terminal type.The new SWIG version 4 is compatible with Basilisk. Install the SWIG software package using:
$ brew install swig
(Optional) If you want to install the HomeBrew version of
cmake, you can do so with:$ brew install cmake $ brew link cmake
(Optional) If you want to install the HomeBrew version of
python3, you can do so with:$ brew install python3
(If using Xcode 11 or higher) Install the ninja utility:
$ brew install ninja
Setting up the Python Environment¶
Note
The following instructions recommend installing all the required python packages in the user ~/Library/Python folder. This has the benefit that no sudo command is required to install and run Basilisk, and the user Python folder can readily be replaced if needed. If you are familiar with python you can install in other locations as well.
Note
If you wish to use the HomeBrew version of python, or generally have multiple copies of python installed on your system, configure the CMake Python paths as described in :raw-latex:`ref `customPython after following these instructions.
Note
We suggest you remove any other python packages (such as Anaconda), or change the path in your terminal shell if you really want to keep it.
In the following instructions, be sure to follow the sequence of tasks as outlined below.
Setting the PATH Environment Variable¶
As this installation will install all required Python packages in the
user home directory Library/Python folder, the PATH variable
must be setup within the terminal environment. If you are using Python 2, then replace 3.7 with 2.7 in the instructions below. It is ok to include both folders in your path if you are using both Python 2 and 3.
Open a terminal window
To open these system files in TextEdit.app for easy editing, you can use the shell
opencommand in steps 3 through 6 belowIf using a Bash shell, then
type:
$ open ~/.bash_profile
Add the line:
export PATH=~/Library/Python/3.7/bin:$PATH
If using a tcsh shell, then
type:
$ open .tcshrc
Add the line:
set path = ( ~/Library/Python/3.7/bin $path )
Save and close the file
Open a new terminal window for the path to take effect
Setup Required Python 2 packages, skip if using Python 3¶
Note
If you already have Python 3 installed and are trying to use Python 2 as well, then depending on the path dependencies the pip command might have to be called with python -m pip to ensure the Python 2 version of pip is called.
First the python package manager
pipmust be installed. From the terminal window, enter the following commands:$ easy_install --user pip
If you run into issues with
pipinstallation setup, you can re-install pip by downloading a fresh copy using:curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
and then executing the following command to install pip in the user’s home directory:
python get-pip.py --user
This step is sometimes needed if you were working with an earlier python installation. Next, install setup tools using:
$ pip install --user --ignore-installed setuptools
Copy the file called
mac_fix_path.pthfrom basilisk/docs to the directory~/Library/Python/2.7/lib/python/site-packages/. For more information about this file see this online discussion.Note
If you have installed python packages already using
sudo pip install, then these are stored inLibrary/Python/2.7/site-packages. You need to add themac_fix_path.pthfile to this folder as well to make macOS ignore the system installed packages. Or, to only use home directory installed python packages, just removeLibrary/Pythonfolder.
Installing required python support packages¶
From the terminal window, install the required general Python packages using either pip3 (for Python 3) or pip (for Python 2):
$ pip3 install --user numpy $ pip3 install --user matplotlib $ pip3 install --user pandas
If using Xcode 11 or higher, then install the meson package using:
$ pip3 install --user meson
Basilisk uses conan for package managing. In order to do so, users must install conan and set the remote repositories for libraries::
$ pip3 install --user conan $ conan remote add conan-community https://api.bintray.com/conan/conan-community/conan $ conan remote add bincrafters https://api.bintray.com/conan/bincrafters/public-conan
Optional Packages: The above directions install the Basilisk base software. There are a series of optional packages that enhance this capability, including
pytestto run an automated test suite of unit and integrated tests.
Pulling and Building the Basilisk Project¶
When all the prerequisite installations are complete, the project can be built as follows.
A Git compatible version control tool like SourceTree should be used to pull/clone the Basilisk repository.
The Cmake.app can’t be used by double clicking on it. The required
conanpaths are not loaded. Instead, runcmakedirectly from the terminal. For Python 3, make adist3destination folder inside the Basilisk directory. Use ‘cd’ to make this your current directory. Then runcmakeusing:$ cmake ../src -G Xcode
If you are using Python 2, then follow the same instructions but make the destination folder
dist. It is ok to have bothdist3anddistfolders. Basilisk is setup such that it can be compiled for both Python 2 and 3. This terminal command will both run theconfigureandgeneratesteps outlined in the next step. You can now skip to step 8. If you have issues runningcmake, especially if switching between python 2 and 3 compiling, trying following the clean build instructions on FAQ.More information is available on Basilisk
cmakeflag options.After successfully running
cmakefrom the command line at least once, you can launch the GUI Cmake.app program from the terminal using:$ open /Applications/cmake.app
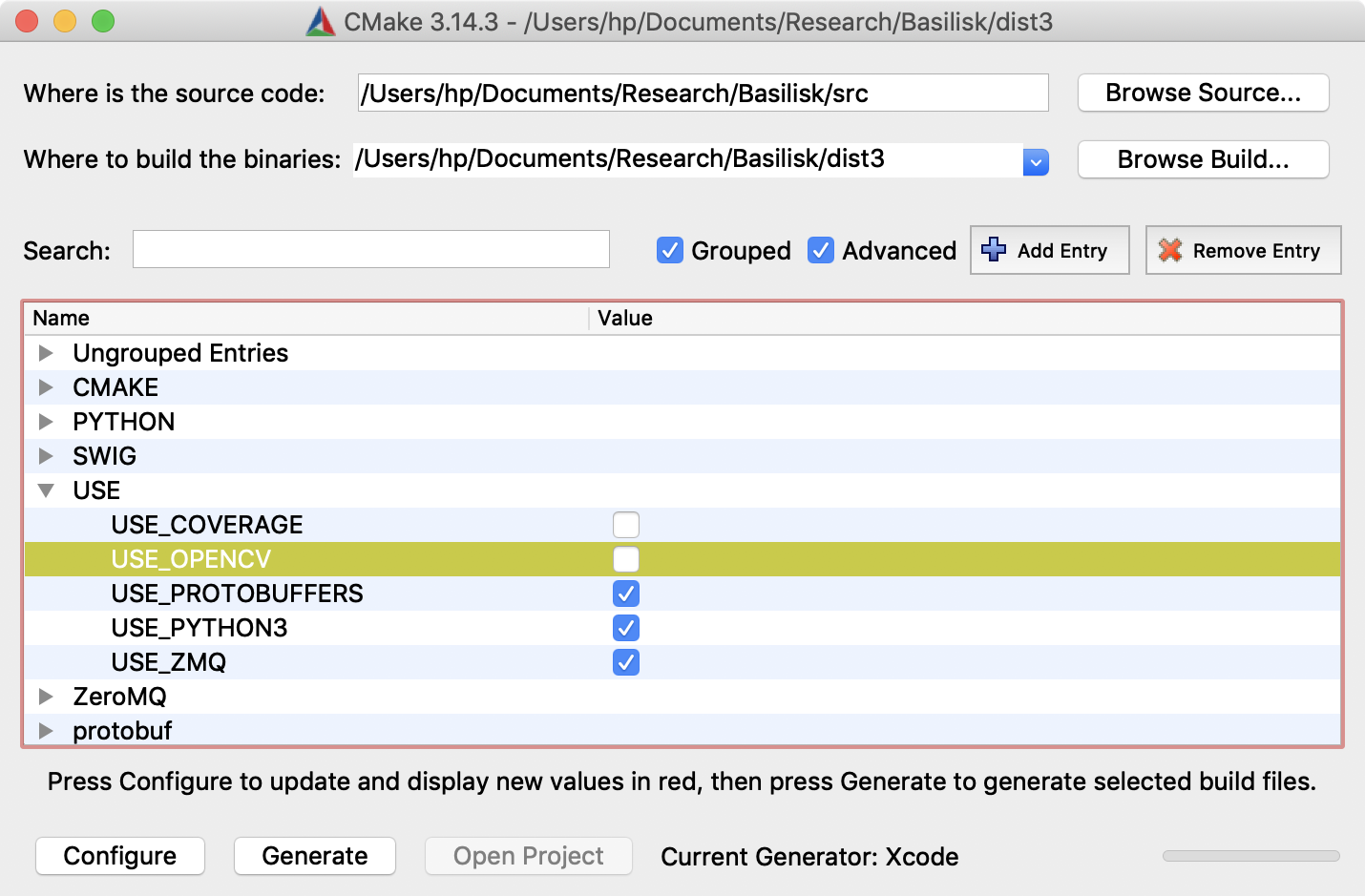
This launches the application with knowledge of the
conanpaths. To use the Cmake.app GUI to create the build files follow these steps:
Click on browse Source, and select the source directory, the Basilisk repository that you just cloned
Browse and select the build directory (
dist3/ordist). If this directory does not exist, create it first.The configuration shown above also enables support to connect with the Vizard visualization.
Press
Configurein Cmake, select the Xcode IDE if running for the first time. If you run into odd errors, try clearing the CMake.app cache under theFilemenu.(Optional) Add a variable named
CMAKE_BUILD_TYPEand set the value to Debug or Release depending on your desired config.Press
Generatein Cmake to build the Xcode Basilisk project file inside thedist3directoryNote
If you wish to use the another version of python configure the Python paths in Using a Custom Python Installation
Warning
If you get an error message in CMake saying it can’t find the compiler tools, open a Terminal window and type:
$ xcode-select -pThis should return:
/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/DeveloperIf instead you get a different director such as
/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools, then correct this compiler directory path using:sudo xcode-select --resetNow clear the Cmake cache and try running
Configureagain.
Open the Xcode project file inside
dist3ordist. This isbasilisk.xcodeprojon macOS.To test your setup you can run one of the example scenario scripts.
For example, in the terminal window, make
basilisk/src/examples/01-OrbitalSimulationsthe current directory.Run one of the tutorial scenarios, such as:
$ python3 scenarioBasicOrbit.py
FAQs¶
Q: swig not installing
A: Make sure you have pcre installed (using brew install preferably)
Q: Experiencing problems when trying to change the directory in which to clone the url
A: clone it in the default directory, and copy it into the preferred one after it is done cloning.
Q : Trouble configuring in Cmake
A: When configuring for the first time, select the appropriate platform for the project (Xcode for instance)
Q : Permission denied when using brew
A: Add sudo to the start of the command. If you do not have superuser access, get superuser access.
Q : Python unexpectedly quit when trying to run pytest
A: Check the python installation. If the path is wrong, uninstall, and reinstall python using brew.
Q : I updated my macOS system to the latest released, and I can no longer run CMake or build with Xcode.
A: Most likely you just need to reset CMake.app to use the latest macOS information. In CMake.app, select File/Delete Cache, and then run Configure again. The application will ask you to confirm the use of the latest macOS and Developer tools.