scenarioBasicOrbitStream¶
Overview¶
This script duplicates the basic orbit simulation in the scenario scenarioBasicOrbit. The difference is that this version allows for the Basilisk simulation data to be live streamed to the About Vizard visualization program.
The script is found in the folder src/examples and executed by using:
python3 scenarioBasicOrbitStream.py
To enable live data streaming, the enableUnityVisualization() method is provided with liveStream
argument using:
vizSupport.enableUnityVisualization(scSim, simTaskName, simProcessName, gravBodies=gravFactory,
liveStream=True)
When starting Basilisk simulation it prints now to the terminal that it is trying to connect to Vizard:
Waiting for Vizard at tcp://localhost:5556
Copy tcp://localhost:5556 and open the Vizard application. Enter this address in the connection field and select
“Direct Communication” mode as well as “Live Streaming”. After this the Basilisk simulation resumes and
will live stream the data to Vizard.
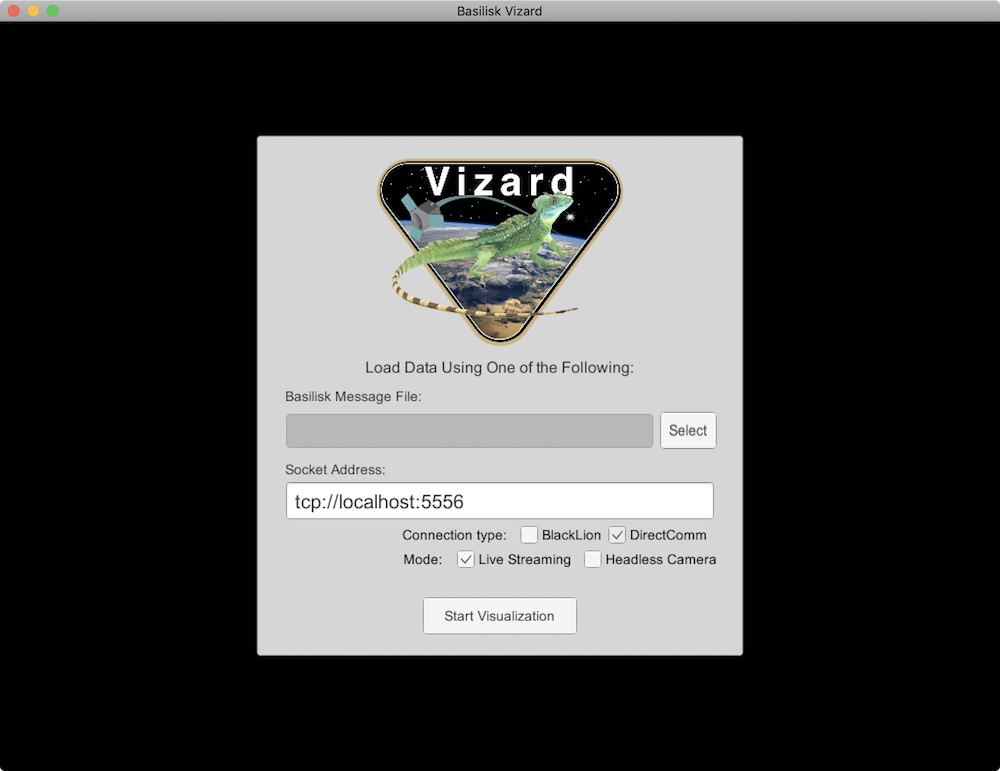
Vizard Direct Communication Panel Illustration¶
To avoid the simulation running too quickly, this tutorial example script includes the clock_sync module that
enables a 50x realtime mode using:
clockSync = clock_synch.ClockSynch()
clockSync.accelFactor = 50.0
scSim.AddModelToTask(simTaskName, clockSync)
This way a 10s simulation time step will take 0.2 seconds with the 50x speed up factor.
-
scenarioBasicOrbitStream.run(show_plots, liveStream, timeStep, orbitCase, useSphericalHarmonics, planetCase)[source]¶ At the end of the python script you can specify the following example parameters.
- Parameters
show_plots (bool) – Determines if the script should display plots
livePlots (bool) – Determines if the script should use live plotting
orbitCase (str) –
String
Definition
’LEO’
Low Earth Orbit
’GEO’
Geosynchronous Orbit
’GTO’
Geostationary Transfer Orbit
useSphericalHarmonics (Bool) – False to use first order gravity approximation: \(\frac{GMm}{r^2}\)
planetCase (str) – {‘Earth’, ‘Mars’}